 Objectives:
Objectives:
- humidity transfer (capillary, convective, liquid) and methods to prevent problems caused by excess humidity
- influence of wind and air tightness on humidity transfer
- the influence of physical characteristics and their succession of materials (λ [Lambda], ρ [Rho], μ [My], w, w₂₄)
- the conditions for mould growth (temperature, moisture, time of exposition)
- humidity input by driving rain / driving snow on surfaces (w1, w₂₄)
- flooding inside (leakages) or outside (surface water on slopes at excessive rainfalls or rivers and lakes overflowing)
- input of humidity by building materials like green wood, pavements, plasters, concrete basement, …
- input of water by plaster/rendering or pavements and walls per m² which has to be dried out during building process
- w1, w₂₄ as to bad storage conditions straw might drop into water on ground (better sort that bales out)
Method:
- lectures, exercises, workshop, group work
Theory:
- lectures, charts, presentations …
Practice/Task:
- explain protection measures of building site with straw from storage to rising walls until rendering is finished and dried
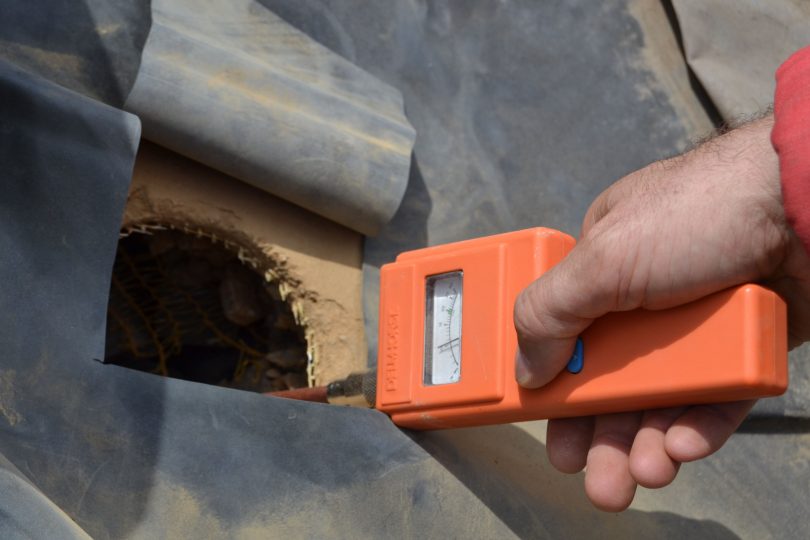
- measuring humidity in straw bales with different tools
- know about drying out (desiccating) time of different materials for plastering on straw per cm layer in average summer climate
Materials/Documents: U6 S5 – Session Plan
Training Time: 3–4 hours







